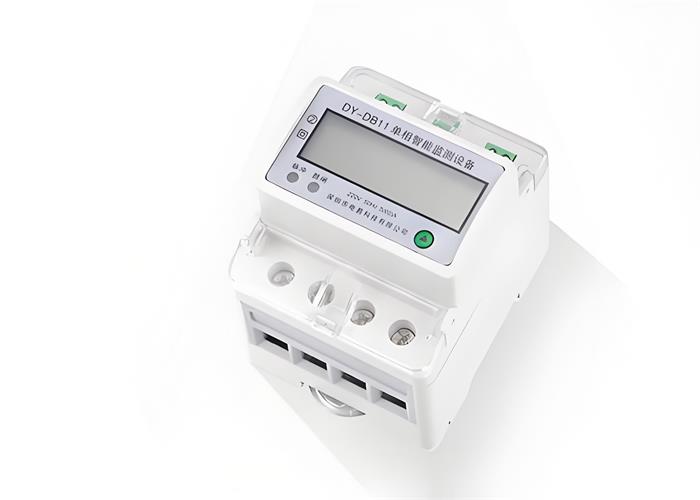
Magnets play a crucial role in National Smart Meter Magnetic Relays, which are essential for accurate power measurement and management. Here’s a detailed look at the applications and functions of magnets in these relays:
1. Basic Working Principle of Relays
Magnetic relays use the principle of electromagnetic induction to control the switching of electrical circuits. The core component of a relay is the electromagnet, and its operation involves:
Electromagnet: The relay contains an electromagnet. When current flows through its coil, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field attracts or repels internal contacts, changing the relay’s switching state.
Moving and Static Contacts: The magnetic field generated by the electromagnet acts on the moving contact (armature), causing it to either make or break contact with the static contact. This process depends on the stable magnetic field provided by the magnet.
2. Applications in Smart Meters
In smart meters, magnetic relays are used in several critical areas:
Power Measurement: Magnetic relays are used for switching control in smart meters to ensure accurate power consumption recording. When the meter needs to perform switching or resetting operations, magnetic relays can quickly respond and execute the necessary switching actions, ensuring accurate data collection.
Load Control: Smart meters may need to control electrical loads or disconnect power supply. Magnetic relays can automatically break the circuit when the load exceeds a preset threshold, protecting the power system's safe operation.
Remote Control and Monitoring: Smart meters often feature remote control and monitoring capabilities. Magnetic relays support these functions by enabling the meter to perform switching operations via remote signals, facilitating remote management and troubleshooting.
3. Selection of Magnetic Materials
Soft Magnetic Materials: Magnetic relays in smart meters typically use soft magnetic materials (such as silicon steel) for the core of the electromagnet. These materials react quickly to changes in the magnetic field, providing a stable magnetic field and enhancing the relay’s response speed and reliability.
Permanent Magnets: Some smart meters use permanent magnets to enhance relay performance. Permanent magnets maintain a stable magnetic field over time, reducing the impact of current fluctuations on the relay, thus improving the meter’s overall stability and accuracy.
4. Advantages of Magnetic Relays
High Precision and Stability: Magnetic relays offer precise switching performance, ensuring accurate power measurement. The stable magnetic field ensures consistent performance under various operating conditions, increasing the reliability of the meter.
Fast Response: Due to the rapid switching capability of magnetic relays, they can quickly respond to changes in current and load. This quick response is crucial for real-time monitoring and control of the power system.
Durability and Reliability: Magnetic relays are typically durable and have a long service life. The stability of magnetic materials ensures reliable operation over time, reducing maintenance and replacement needs.
5. Examples in Smart Meters
Power Metering Instruments: In smart power metering instruments, magnetic relays handle current measurement, load control, and data recording. They ensure the meter accurately records power consumption data and performs load switching or disconnection when required.
Smart Grid Systems: In smart grid systems, magnetic relays facilitate communication and control between the meter and other devices. They help the meter interact with the grid, supporting remote monitoring and control, thus improving the efficiency and stability of the power system.
Summary
Magnets are vital in National Smart Meter Magnetic Relays, enabling precise control and accurate measurement of electrical parameters. They support key functions such as power measurement, load control, and remote management. The choice of magnetic materials and their application ensure high precision, fast response, and reliable performance, enhancing the overall functionality and stability of smart meters and power systems.




 English
English