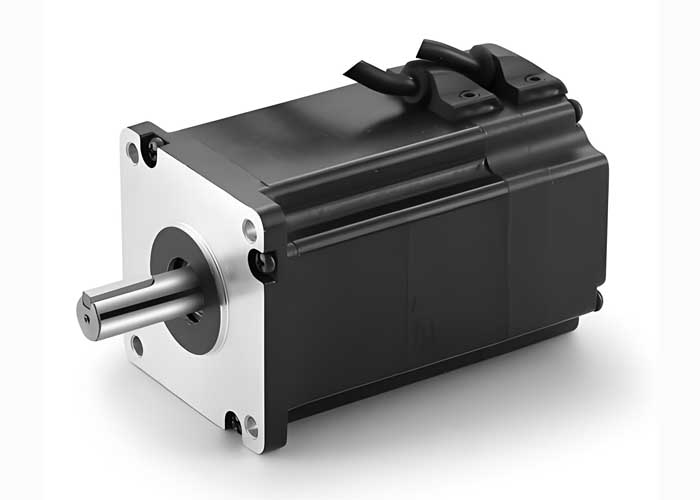
Magnets play a critical role in the operation and efficiency of Brushless Motors (BLDC motors), which are widely used in various applications due to their reliability and performance. Here’s an in-depth look at how magnets are utilized in brushless motors:
1. Basic Principles of Brushless Motors
Brushless DC motors (BLDC motors) differ from traditional brushed motors by eliminating the brushes and commutator. Instead, they use electronic controllers and permanent magnets to achieve motor operation. The key components involved include:
Stator: The stationary part of the motor, which includes coils of wire that are energized to create a rotating magnetic field.
Rotor: The rotating part of the motor, which contains permanent magnets.
2. Magnet Placement and Configuration
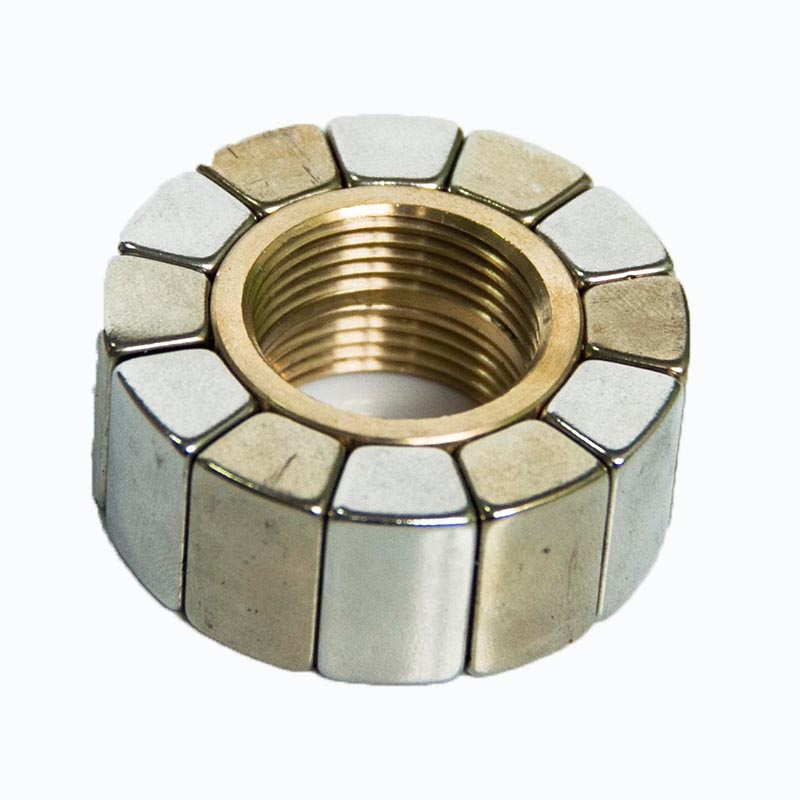
Permanent Magnets on the Rotor: The rotor of a brushless motor is equipped with permanent magnets. These magnets are typically made from materials such as neodymium or Ferrite, known for their strong magnetic properties. The arrangement and placement of these magnets are crucial for the motor's efficiency and performance.
Magnet Types:
Neodymium Magnets: These are high-performance magnets that offer strong magnetic fields relative to their size. They are commonly used in brushless motors for their superior magnetic strength and compact size.
Ferrite Magnets: These are less expensive and provide sufficient magnetic strength for many applications. They are often used in motors where cost is a significant factor.
3. Motor Operation
Magnetic Field Interaction: In a brushless motor, the stator windings are energized in a sequence controlled by an electronic speed controller (ESC). This energizing creates a rotating magnetic field. The permanent magnets on the rotor interact with this rotating field, causing the rotor to turn.
Commutation: The electronic controller manages commutation by switching the current through the stator windings in synchronization with the rotor’s position. This precise timing ensures smooth rotation and efficient operation.
4. Advantages of Using Magnets in Brushless Motors
High Efficiency: Permanent magnets contribute to the high efficiency of brushless motors by minimizing energy losses. Unlike brushed motors, where friction and wear can lead to energy dissipation, brushless motors utilize magnetic fields without physical contact, resulting in less energy loss.
Reduced Maintenance: The absence of brushes in brushless motors eliminates the wear and tear associated with brush and commutator systems. This leads to reduced maintenance needs and longer motor life, as there are fewer parts subject to mechanical degradation.
Higher Power Density: Permanent magnets provide a strong magnetic field, which contributes to the high power density of brushless motors. This means that brushless motors can deliver more power relative to their size and weight compared to brushed motors.
5. Applications of Brushless Motors
Consumer Electronics: Brushless motors are used in various consumer electronics, such as computer cooling fans, drones, and electric vehicles. Their efficiency and reliability make them ideal for applications where performance and longevity are critical.
Automotive Industry: In electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, brushless motors are employed for propulsion and various ancillary functions. Their high efficiency and low maintenance requirements are well-suited for automotive applications.
Industrial Applications: Brushless motors are used in industrial machinery and robotics due to their precision and reliability. They are commonly found in applications requiring precise control and high torque, such as CNC machines and automated manufacturing systems.
Aerospace and Defense: The aerospace and defense sectors use brushless motors in various applications, including actuators and flight control systems. Their reliability and performance are crucial for the demanding conditions of aerospace environments.
6. Magnetic Design Considerations
Magnet Size and Shape: The size and shape of the permanent magnets influence the motor’s performance. Larger magnets or magnets with specific shapes can enhance the motor’s torque and efficiency. The design must balance magnetic strength with the physical constraints of the motor.
Magnet Material: The choice of magnet material affects the motor’s performance characteristics. High-energy materials like neodymium provide strong magnetic fields and are preferred for applications requiring high power and compact design.
Thermal Management: Permanent magnets can experience a reduction in magnetic strength at high temperatures. Effective thermal management is essential to ensure the motor operates efficiently under various conditions. This includes using materials that can withstand temperature fluctuations and designing the motor to dissipate heat effectively.
7. Future Developments and Innovations
Advanced Materials: Ongoing research aims to develop advanced magnet materials with higher magnetic flux densities and improved temperature stability. These innovations will enhance the performance of brushless motors and expand their applicability.
Integrated Electronics: Future brushless motors may integrate advanced electronics directly into the motor assembly. This integration could streamline design, reduce size, and improve overall performance by optimizing the interaction between the motor and its control system.
Summary
Magnets are fundamental to the operation of brushless DC motors, contributing to their high efficiency, reduced maintenance, and power density. Permanent magnets on the rotor interact with the stator’s rotating magnetic field to produce motion, enabling a wide range of applications from consumer electronics to industrial machinery and aerospace systems. By leveraging the benefits of permanent magnets and continuously advancing material and design technologies, brushless motors are poised to continue their pivotal role in various fields.




 English
English