Magnets in New Energy Vehicles as well as Conventional Vehicles
Magnets play a crucial role in both electric vehicles (EVs) and traditional automobiles. Here are some key applications:
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
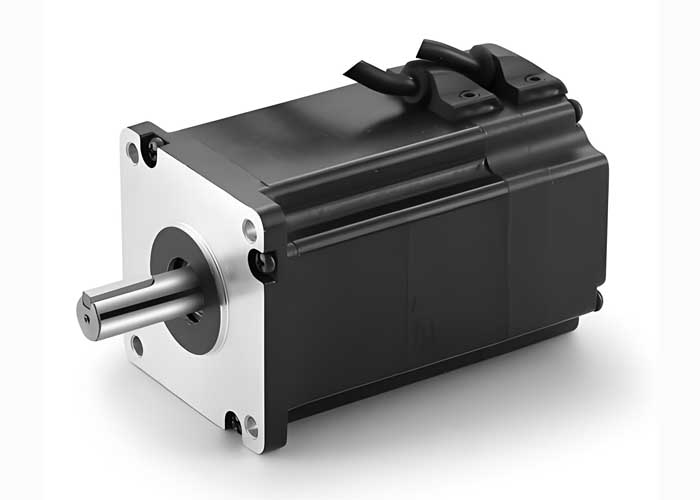
Electric Motors (Electric Drive Systems): In EVs, magnets are essential in electric motors, especially in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs). Permanent magnets provide the necessary magnetic field for the motor, enhancing efficiency and power density.
Sensors and Switches: Various magnetic sensors, such as Hall effect sensors, are used in EVs for battery management systems (BMS), motor control, and vehicle stability control systems. These sensors monitor parameters like current, speed, and position.
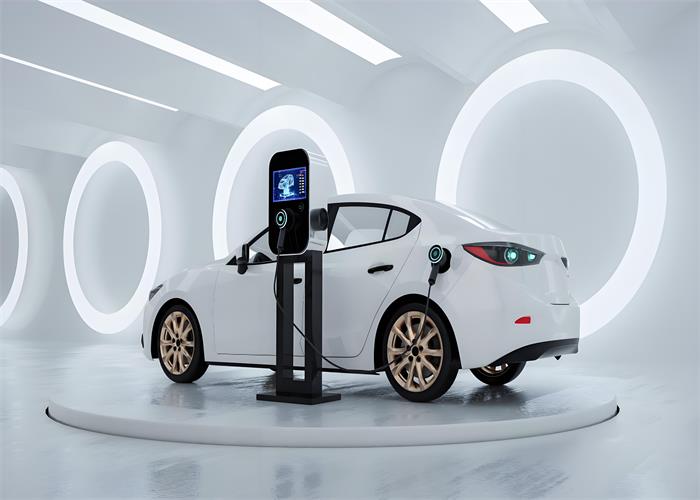
Wireless Charging: EV wireless charging systems use magnetic fields to transfer power between the charging pad and the vehicle. The system includes a transmitter coil and a receiver coil, with magnets ensuring efficient alignment and transfer.
Battery Management: Magnetic sensors and components are used in BMS to monitor battery conditions such as temperature and current, ensuring safety and performance.
Traditional Vehicles
Starter Motors and Alternators: In traditional vehicles, magnets or electromagnets are used in starter motors and alternators to generate electromagnetic fields, which are crucial for starting the engine and generating electrical power.
Power Windows and Door Locks: Magnets are used in power window motors and electronic door locks to enable smooth operation and secure locking mechanisms.
ABS Systems: Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) use magnetic sensors to monitor wheel speed and prevent skidding, ensuring better vehicle control during braking.
Ignition Systems: In older ignition systems, magnets are used in ignition coils to generate the high voltage needed to spark the engine.
These applications demonstrate the significant role of magnets in enhancing the functionality and performance of both electric and traditional vehicles.




 English
English